Is The Cash Industry Dying? - CMS Infosystems
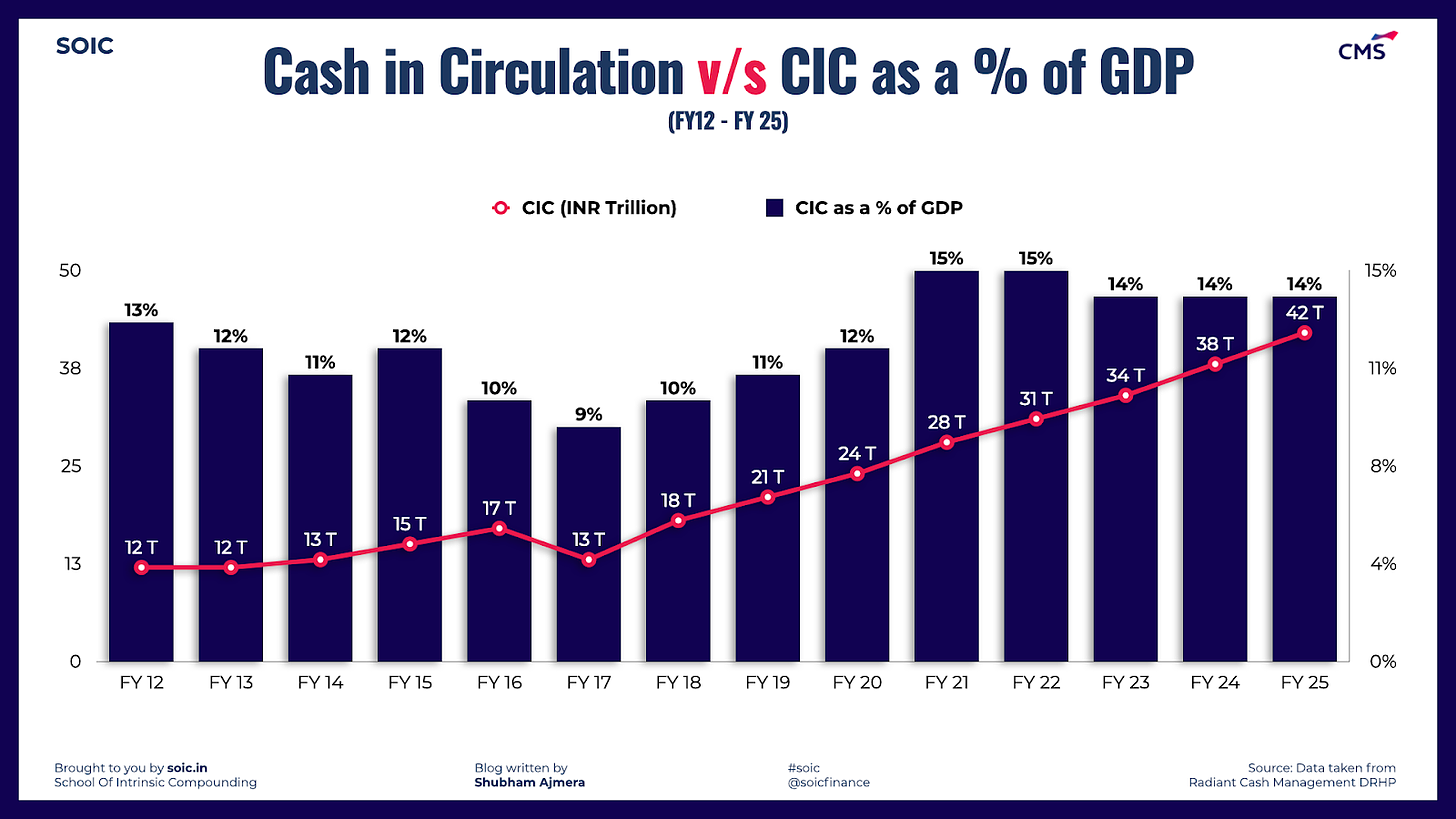
One common perception we have seen among many individuals including me till few weeks ago was that post demonetisation and increase in digital payments with introduction of UPI, cash usage has came down drastically in last 2-3 years as I was using Gpay and PhonePe for almost all my day-to-day transactions and I was looking at the whole industry with my viewpoint only, but then reality struck & got to know that I was in my own virtual world and reality is something else. Last week RBI issued numbers of the cash in circulation (sum of cash held by banks and currency held by the general public) in October 2021 has increased to ₹30.88 lakh crore which is 71.84% higher than the level for the fortnight ended November 4, 2016. On November 8, 2016, Prime Minister Narendra Modi had announced the decision to withdraw ₹500 and ₹1,000 denomination notes.
As per RBI report this can further rise to ₹41.5 lakh crore by FY 25 with an expected CAGR growth of 9.95%.
With the help of above mentioned data we are looking for some opportunity in the sector and companies which can benefit from this, we will be analysing one such business today:
CMS Info Systems Ltd.
CMS Info Systems Limited (“CMS”) was incorporated on March 26, 2008. CMS Info Systems is a leading business services company catering to the BFSI, Retail and Logistic Sectors. CMS is India’s largest cash management company based on number of ATM points and number of retail pick-up points, as well as one of the largest ATM cash management companies worldwide based on number of ATM points.
It installs, maintains and manages assets and technology solutions on an end-to-end outsourced basis for banks under long term contracts. It caters to a broad set of outsourcing requirements for banks, financial institutions, organised retail and e-commerce companies in India.
Business Segments of the Company:
The company operates its business majorly in two segments namely Cash Management Services and Managed Services and Card Personalization:
Cash Management Services:
It includes end-to-end ATM replenishment services, cash pick-up and delivery, network cash management and verification services (together known as “retail cash management services”), and inter-city and intra-city movement of currency, and cash-in-transit services for banks. This segment accounts for 69% of revenue for the FY22.
CMS’ cash management business comprises ATM cash management, retail cash management, cash-in-transit services and other cash management services, which the company carries out through two distinct brand names, CMS and Securitrans.
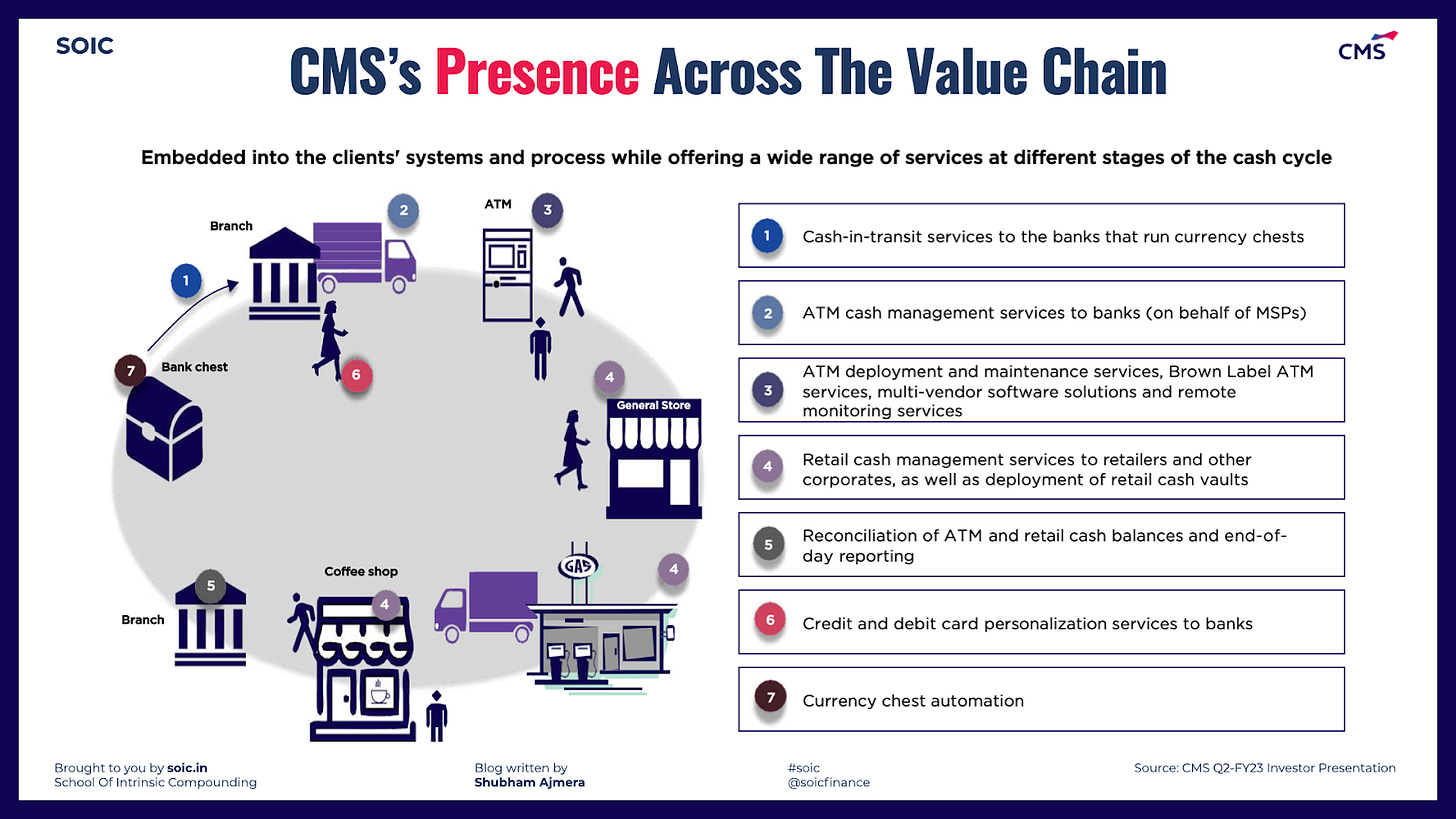
CMS is present across the value chain of Cash Management:
ATM Cash Management Services – It primarily includes cash withdrawal from banks, ATM replenishment, cash evacuation & deposition for cash deposit machines & cash recyclers, end-of-day reporting, reconciliation & settlement and first line maintenance services that are necessary to return the ATM machine or its infrastructure to proper operating condition, such as removing jams or refilling paper rolls.
Retail Cash Management Services – It includes outsourced retail cash pick-up, retail currency processing, retail cash vaults, automated cash vault solutions and smart safe solutions for over 2,000 customers either directly or through banks. Customers for these services are primarily banks that offer banking services to insurance providers, NBFCs, restaurants, utilities, e-commerce companies, logistics providers, government establishments, fuel stations, consumer goods companies and hospital chains.
Cash in Transit Services – It includes inter-city and intra-city transport of cash. The pricing model for cash-in-transit business is for a fixed fee per month plus additional fees, depending on what extra operations, based on time and distance, are required). On account of RBI and MHA guidelines, banks are shifting from unorganized to organized compliant service providers which has increased the demand for larger players.
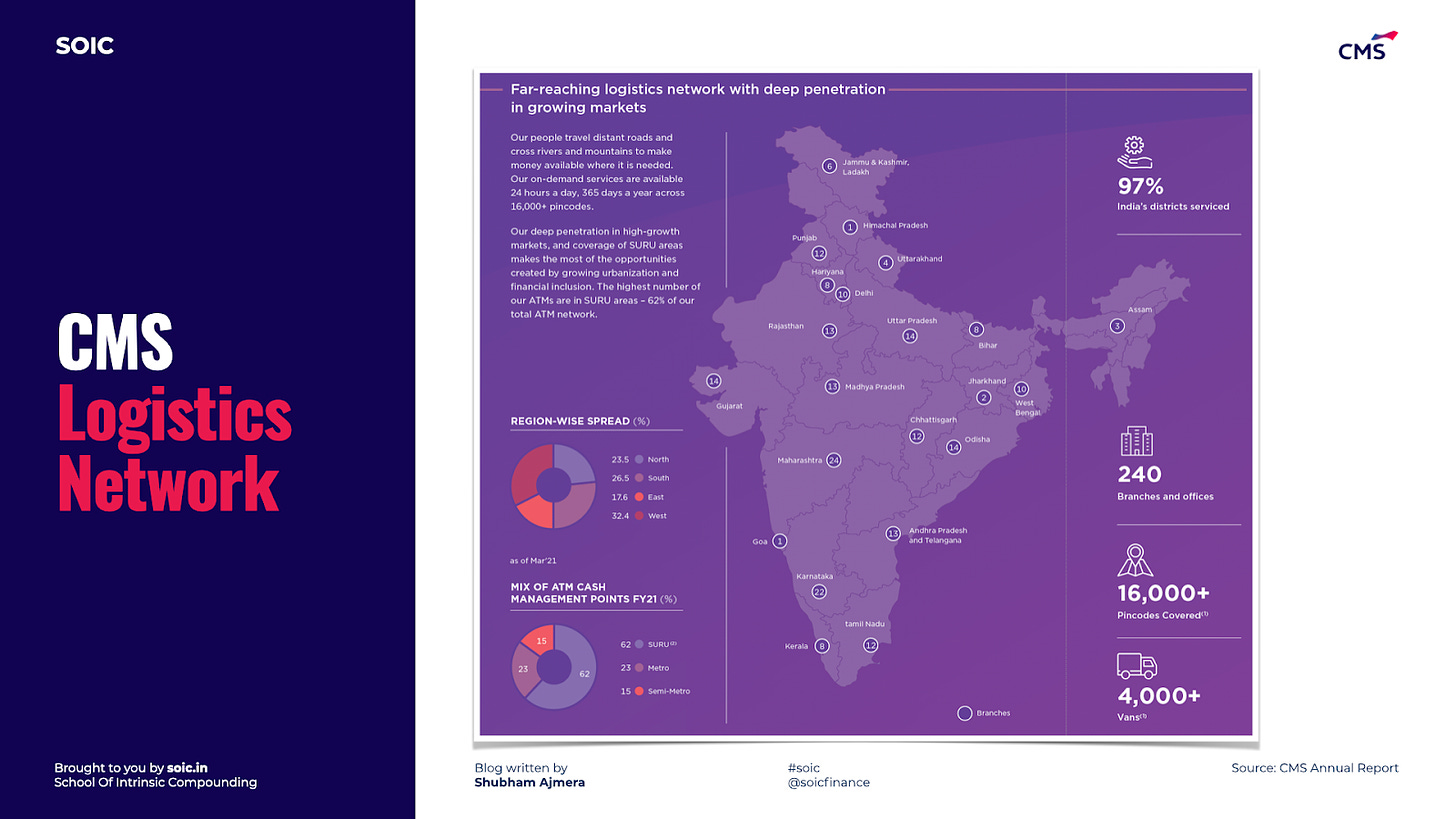
CMS had a pan-India fleet of more than 4,000 cash vans with a network of 240 branches and offices, covering all states and union territories in the country with 97% of India’s districts and covering more than 16,000 Indian postal codes, which enabled it to take advantage of future growth opportunities. Through its network, it served more than 150,000 business points across its ATM cash management, retail cash management, and managed services businesses in FY22.
Managed Services and Card Personalization:
Managed services include banking automation product sales, deployment and associated annual maintenance, end-to-end Brown Label deployment and managed services for banks, common control systems and software solutions, including multi-vendor software solutions and other security and automation software solutions as well as remote monitoring for ATMs. It also provides end-to-end financial cards issuance and management for banks and card personalization services. This segment accounts for 31% of revenue for the FY22.
CMS is one of the few companies in India that can offer end-to-end management of an ATM network, from both an operational and a management perspective, through a single point of accountability. The business is largely recurring in nature with long term contracts, which provide high revenue visibility for its managed services business.
ATM managed services allow financial institutions to take advantage of dedicated managed service providers' infrastructure, experience, scale and product portfolio to increase the effectiveness and efficiency of the financial institutions' networks of ATMs.
ATM managed services cover a wide range of services, from specific operational components to end-to-end ATM programme management. As the ATM market continues to shift from bank-managed ATMs to end-to-end deployments of ATMs by service providers, the business of outsourcing ATM management is expected to grow fast in India. ATM Managed services include products sale and maintenance (ATMs, cash recyclers, automation products), ATM software solutions (multivendor software, endpoint security, and reconciliation software), Brown-label ATMs service, Pure Managed Services, and ATM remote monitoring.
Banking automation product sales and service (AMC) – It includes ATM sales, where the company offers customers a variety of bank automation products through cooperation with various OEMs, as well as product deployment, service and AMC support through the product life cycle. Its product offering includes ATMs, cash recyclers, passbook kiosks, teller cash recyclers; Many public and private banks in India are expected to update and expand their ATM networks, and CMS intends to build on this arrangement and win a larger share in the ATM update and expansion cycle.
Brown label ATM (BLAs) and pure managed services – In BLAs, the hardware of the ATM machine is owned by the service provider who is responsible for selecting ATM locations, negotiating a lease arrangement with the landlord and providing power to the ATM kiosk. As a result, the service provider is responsible for deployment and end-to-end ATM management, while the sponsor bank is responsible for providing cash and access to the banking network. Banks pay on a fixed monthly fee model or a pay per transaction model.
CMS includes Brown Label ATM services, where the company deploys, maintains and manages ATMs on an end-to-end basis under a bank’s brand name and provide ATM infrastructure to bank customers who pay on an ongoing, day-to-day operational basis, as well as pure managed services, where it manages ATMs owned by banks on an 'asset-light' basis, including through the provision of services such as second-line maintenance, reconciliation, Electronic Journal (EJ) management, cash forecasting, among others.
Both PSBs and private sector banks are expected to adopt BLAs as it offers significant convenience with a reduction in capex.
Software solutions – It includes ATM multi-vendor software solutions, ATM software upgrade services and proprietary software solutions for risk management and transaction reconciliation.
Remote monitoring for ATMs and bank branches - Company does remote monitoring through centralized monitoring centres by deploying cameras and advanced sensors on site with a provision for quick response function upon detecting any threats or adverse events. The company’s corporate customers include new-age, tech-enabled companies as well as traditional businesses across various industry verticals such as BFSI, telecom, FMCG, industrials, logistics and transportation.
ATM remote monitoring includes video remote monitoring of sites (live and trigger-based), distributed or centralised, typically harnessing a two-way audio mechanism and access to quick response teams. Beyond conventional services, remote monitoring could also include other value-added services such as video analytics, customer behaviour information, remote camera health monitoring, IoT, etc.
Other Services: CMS other business includes end-to-end financial card solutions for banks. It primarily involves sourcing plastic cards and chips and personalizing the cards with embossing & printing, uploading variable encrypted data on the chip or magnetic stripe. The company is also involved in data generation for card personalization, card & chip personalization programs, cryptographic key management solution, consultancy for migration and instant card issuance capabilities.
CMS has also developed proprietary card personalization management software called “CPMS Gnxt Software”, which was developed in-house and is used by banks issuing credit and debit cards. The card personalization is done at facilities that have been certified by two global card payment networks, and the product offering includes credit cards, debit cards, as well as smart cards, and the company has expertise in handling various types of smart card issuance programs.
Key growth triggers and competitive advantage for the company are as follows:
Leading player in a consolidating cash management market: India is the third largest ATM market in the world based on number of installed ATMs, after China and the United States, and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.16% from 255,000 as of March 31, 2021 to 365,000 as of March 31, 2027.
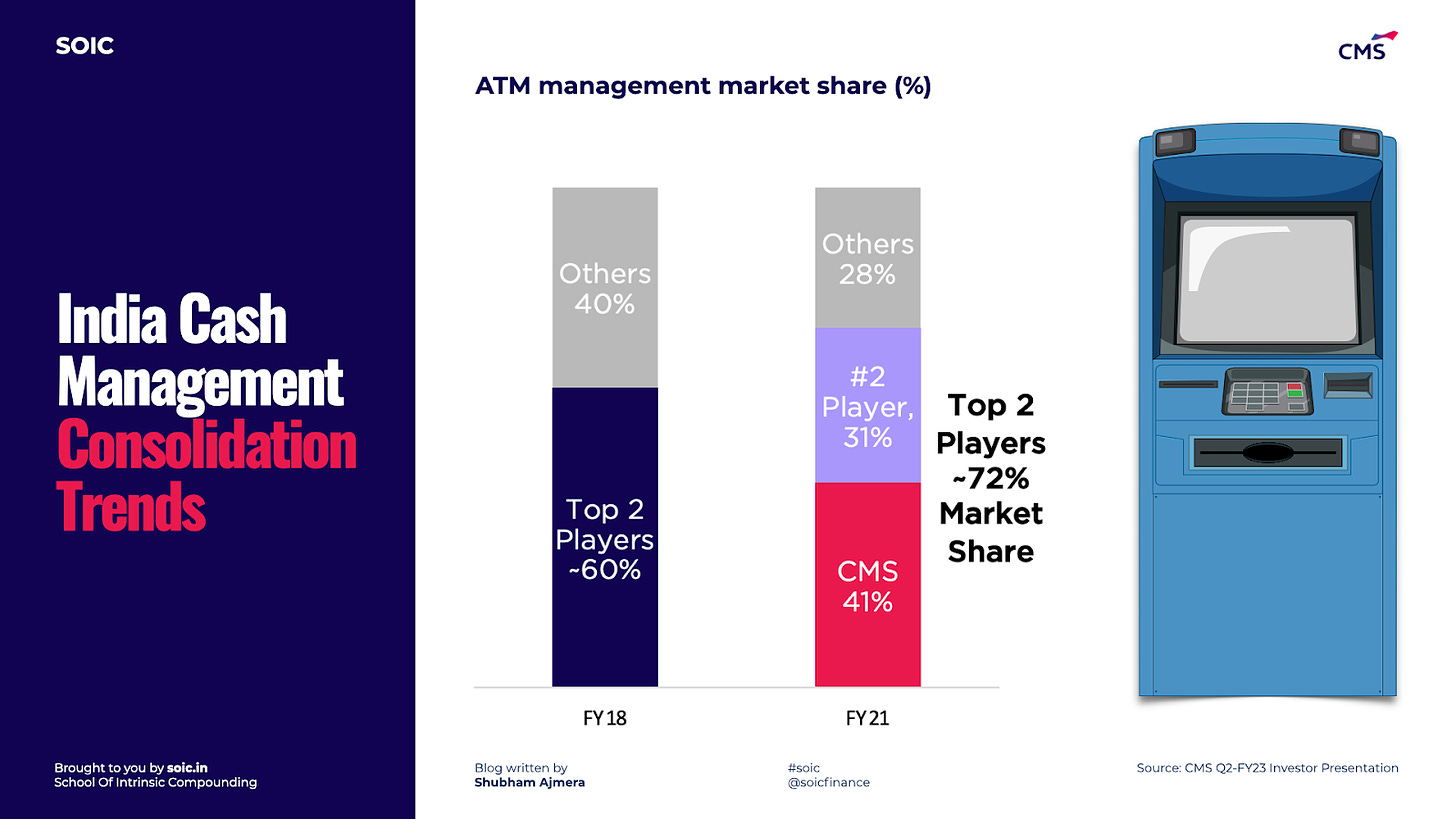
The cash management industry in India has continued to consolidate in recent years, with a number of large and medium scale mergers and acquisitions, resulting in the two largest companies (incl. CMS) in the industry increasing their aggregate market share with respect to the ATM segment from ~60% in FY18 to ~72% in FY21.
The industry is consolidating due to changes in regulations that ensure cash management companies meet operating standards with respect to the handling of cash, as well as trends in customer preference favouring larger cash management companies with more scale and stable operations. CMS is India’s largest cash management company based on number of ATM points and retail pick-up points with a market share of 24.7% based on the total number of ATMs (41.1% based on the total number of outsourced ATMs). In the cash management industry, there is a positive correlation between market share, network size and profitability.
Growing cash cycle and replacement demand for ATMs: As the amount of cash in circulation increases, so does the need for cash and cash-related services, and cash in circulation in India increased at a CAGR of approximately 10% - 12% Y-o-Y from FY01-21. The RBI, in its half-yearly Monetary Policy Report released in October 2021, indicated that among the various modes of retail payments in India, the volume of transactions through ATMs, credit cards and debit cards has a high correlation with India’s GDP.
The increase in demand for cash and cash-related services in India is expected to cause banks and other participants in India to deploy more ATMs. The number of ATMs in India is expected to increase from 255,000 as of March 31, 2021 to 365,000 as of March 31, 2027, leading to 6.2% CAGR growth.
These trends have caused and will continue to cause banks and other market participants in the cash management market, managed services and across the cash cycle in India to increase the automation of their banking services and their outsourcing of cash management, managed services and other banking services. ATM outsourcing is expected to increase as PSBs increasingly focus on core business and operations. Further, the current base of ATM and cash management assets of banks are coming up for renewal and replacement over the next three years, given the average life spans of ATMs and since a large portion of ATMs in India were installed in 2013 and 2014.
Many banks are outsourcing their ATM servicing requirements on an end-to-end basis, including with respect to cash replenishment, and CMS with its presence across the entire ATM and cash management value chain can offer integrated service and product offerings to its customers.
Pan-India footprint with deep penetration in growing markets: CMS’s pan-India fleet of 4,000+ cash vans and its network of 240 branches and offices, cover all of India’s states and union territories, with 16,000+ pin codes covered. India has one of the lowest ATM penetration rates in the world, with only 22 ATMs per 100,000 adults, compared to a global average of 47 ATMs per 100,000 adults as of 2020. ATMs, in particular in semi-urban/rural regions where ATM penetration is very low at 15 ATMs per 100,000 adults as of December 31, 2020. In addition, the government's financial inclusion programs, including Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana and other direct benefit transfers, provide direct benefits and subsidies to populations in semi-urban and rural areas and is expected to result in an increase in cash withdrawals and a higher demand for ATMs in those areas in the future, requiring banks to deploy and outsource a greater number of ATMs. These initiatives have increased and will continue to increase the number of cash transactions in these regions, as well as demand for cash management services and ATM sales and maintenance services.
CMS was among the first cash management companies to invest in the growth of its business in rural and semi-urban areas in India, and its Pan-India footprint enables it to offer its services to its customers in these areas as they grow their businesses and take advantage of opportunities created by these government initiatives and the expansion of the banking network in India. Its platform offers customers a single point of reference across India for their operations, as well as an integrated service offering. The geographic reach of ATM cash management services providers is a key purchasing criteria for banks as well.
Remote monitoring opportunity in BFSI to quadruple by FY27: As a part of the managed services business, CMS offers remote monitoring for ATMs and bank branches through centralised monitoring centres by deploying cameras, advanced sensors and other value added services such as video analytics, customer behaviour information, remote camera health monitoring, IoT etc. The company entered into the ATM remote monitoring business in 2021 and are now live at about 18,500 locations as of September 2022.
CMS’s remote monitoring systems utilize proprietary software to detect potential threats remotely using AI and self-learning technology. The remote monitoring opportunity is expected to grow at 25% CAGR over FY21-27 from INR 800 cr to INR 3,000 cr. CMS intends to leverage its remote monitoring technology to differentiate its product offering and target sectors beyond only the ATM and banking sectors, such as the retail, warehousing and industry sectors, where it expects that demand for remote monitoring will continue to grow.
Expand into business areas that create synergies with current business: CMS has an established track record of incubating new businesses and scaling up business in business areas where it identifies opportunities for potential growth, whether in a new business area or in areas where CMS has existing operations.
Many public and private banks in India are expected to update and expand their ATM networks, and it intends to build on this arrangement in the future and compete aggressively to win a larger share in the ATM update and expansion cycle. It also expanded into multi-vendor software solutions in 2019 and has deployed it across ~50,000 ATMs as of March 31, 2022 of India’s largest bank, State Bank of India and intends to continue targeting other large public sector banks in India in this sector.
CMS has also identified and are in the process of expanding three other new business areas, which include remote monitoring outside of the ATM and banking sectors, end-to-end currency management and financial services distribution:
Remote monitoring (outside the ATM and banking sectors): CMS intends to leverage its remote monitoring technology to differentiate its product offering and target sectors beyond only the ATM and banking sectors, such as the retail, warehousing and industry sectors, where it expects demand for remote monitoring will continue to grow.
End-to-end currency management: CMS end-to-end currency management services for banks include cash processing at currency chests for counting, sorting, checking note fitness, packaging, among other services; end-to-end management of currency chest for banks and NBFCs, including providing manpower and transport at various locations; and services for white-label currency chests. It is well-placed to continue to expand into end-to-end currency management services for banks by leveraging its strong market position in the cash management segment.
Financial services distribution: A key focus of CMS’s business strategy is financial services distribution, which includes corporate business correspondent ("CBC") services, in which it intends to provide banking-related services, such as cash withdrawals and deposits, payments, KYC, account opening, retail payments, among other things, in areas that are less served by banks by recruiting and managing business correspondents on behalf of banks; fulfilment of financial services on behalf of banks and NBFCs by leveraging its existing infrastructure in order to fulfil financial services being offered by banks and NBFCs, such as on demand pickup and doorstep banking services, NBFC soft loan collections and disbursement; and commission agent services on behalf of banks and NBFCs, which includes distribution of financial services (in particular loans) with end-to-end process management, including services such as lead generation, KYC and documentation, gold appraisal, storage and custody, but excluding underwriting, for a commission on the disbursed value amount.
Payment Solutions: CMS intends to use its banking relationships and technology capabilities to develop and commercialize a wide array of differentiated payments solutions, including bill payments, POS networks, digital payments and other merchant payment solutions, and micro-ATM offerings. In addition to its core strengths, it intends to evaluate acquisition targets and develop partnerships to roll out these services.
History of the company:
The company was incorporated in 2008 as Subhiksha Realty Private Limited, subsequently in December 2008 they changed the name of the company to CMS Info Systems Private Limited’.
In 2009 The IT infrastructure management division of CMS Computers Limited was demerged and transferred to the Company followed by an investment by the Blackstone Group to acquire a majority stake in certain key businesses of CMS Computers.
In 2011 the company acquired Securitrans India Private Limited, thus consolidating its position as the leading cash management services company in India
In 2015 Sion Investment Holdings Pte. Limited, an affiliate of Baring Private Equity Asia acquired 100% stake in CMS Info Systems and became the promoter of the company.
Company is headed by Mr. Rajiv Kaul who has been associated with CMS since inception and has over 29 years of experience across the technology, private equity and business services sectors.
Prior to his association with CMS, he worked with Actis Capital LLP, London, as a Partner and with Microsoft Corporation (India) Private Limited as its Managing Director, India, from where he moved to Redmond, USA as Senior Director (Emerging Markets). He was formerly a member of RBI’s Committee on Currency Movement which was constituted post demonetisation. In the past, he has been associated with National Association of Software and Service Companies (NASSCOM) as an elected member to the Executive Council and also as a member of the National Council of CII from 2003 to 2005. He is also a member of the General Council of Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra.
Key Risks in the business:
Decrease in the availability/use of cash: The use of payment options other than cash, including credit cards, debit cards, POS terminals, stored-value cards, mobile payments and online purchase activity has increased significantly in India in recent years and a continued shift in consumer trends in India with respect to the use of cashless payment methods could result in a significant reduction in the use of cash.
Cashless transaction is an irreversible revolution that India is experiencing currently. It’s riding on the back of change in habits of Indian consumers, increasing smartphone penetration levels and the country's potential for growth. Its fortunes are closely linked to the growth of consumerism in India. On top of that, millennials in India are leading this change from front. I personally believe that this new way of doing monetary transactions will keep on increasing in the years to come.
Government of India (GoI) and Reserve bank of India (RBI) are undertaking initiatives to encourage greater adoption of electronic and cashless payment methods. Notably, RBI has set out in its ‘Payment and Settlement Systems in India: Vision 2019-2021’ statement that it is undertaking strategic initiatives to encourage greater adoption of cashless payment methods to empower every person in India with access to e-payment options.
Further, if RBI introduces a digital currency in the future, it may also impact the amount of cash in circulation. A reduction in cash in circulation or need for less cash to be transported and a decrease in the number of ATMs to be deployed/serviced can reduce the need for CMS’ cash management services and managed services business. Though management is confident that it will not affect their business.
However, recent data suggests that despite the surge in digital transactions, cash in circulation has grown 10% YoY as of Mar '22 to hit an all-time high of INR 31trn.
Regulated by RBI and GoI: The business is highly dependent on the banking sector in India which is regulated by RBI and GoI and any adverse development with respect to Indian banks that adversely affects their utilisation of and demand for cash management services or their deployment or utilisation of ATMs could have an adverse effect on the business.
NeoBanks: Neobanks are all-digital banks that deliver services to their customers through digital media. There are no physical branches, unlike traditional banks, and all transactions are completed through digital or mobile-only platforms only. These new digital banks are gaining popularity in developed countries. Our central bank will take a pragmatic view on this concept sooner than later.
Customer concentration risk: CMS’ top-3 and top-5 customers contributed to more than 40% and 55% of its revenue. If one or more of its key customers were to suffer a deterioration in their business, the company’s business would be impacted. Loss of its key customers/inability to renew contracts/decision by its key customer to reduce services from CMS may result in a decline in CMS’ revenue.
Valuations of the Company:
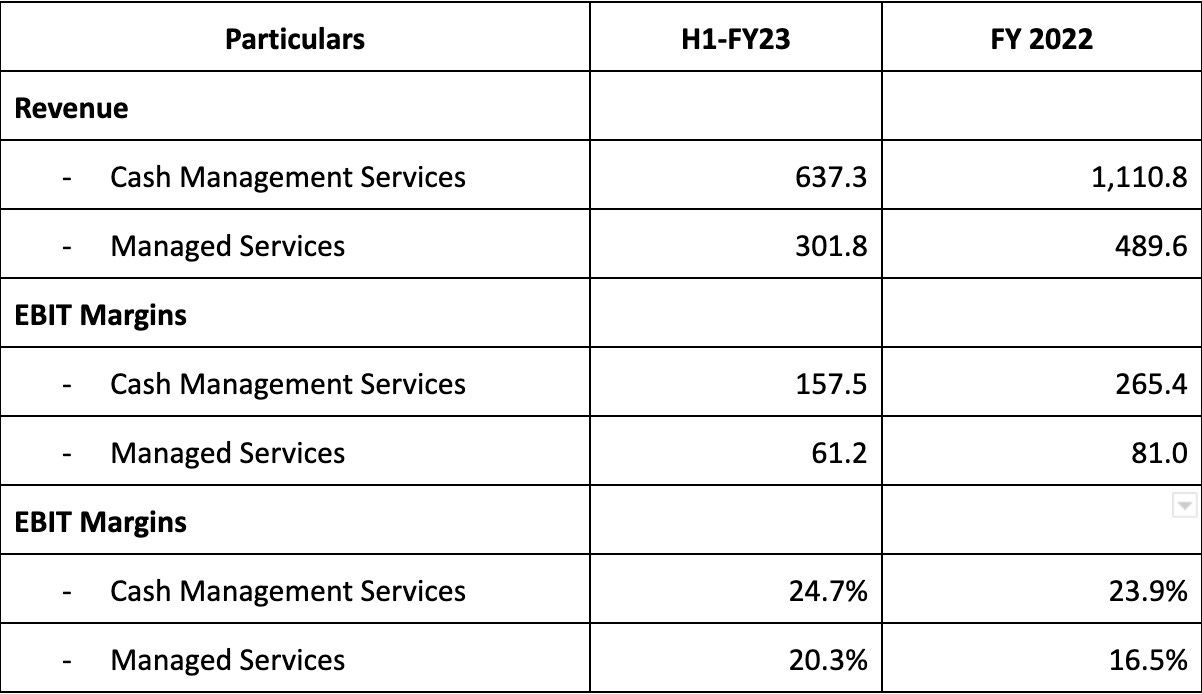
As discussed the company has 2 major segments the revenue and margins of same are as follows:
Currently the major revenue contributor for the company is cash management services however the growth in managed services is faster and management is also trying to increase its share in total revenue contribution as this segment is a recurring business where they have fixed long term contracts.
At the time of writing the company is valued at 20 times Price to Earnings ratio and EV to EBITDA of 10.6 times. The order book as on September 2022 is more than 2800 crores. The company has guided for the revenue of 2500 cr to 2700 cr for FY25.
I have done a brief bull/bear/base scenario analysis for the business in the google sheet below. Feel free to play around with the assumptions.
SheetLink- https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/15zb2zTir0ZDxPKiJ9MMlweenP5kCqsbOdsgw4Odo0Ts/edit?usp=sharing
Since cash is a dying industry in the long term, in my opinion it will not get high valuations unless they are able to increase the managed services segment to more than 50%, hence I have given it a EBITDA multiple of 10 to 12 times.
Do let us know in the comment section below your views on the valuations of the company and how much PE or EBITDA multiple you will ascribe to such companies.
Disclosure: Nothing on this website should be construed as investment advice. Please consult your financial advisor. We are not SEBI registered Analysts/Advisors. We are not accountable for any loss or gains that might occur to you from this or any analysis on the website. The author and SOIC do not hold the stocks in their portfolio at the date this post was published.
AUTHOR
Shubham Ajmera
Shubham Ajmera is a Chartered Accountant by profession working as equity research analyst with SOIC.